How to Access a Server on Your Local Network: A Technical Guide
Accessing a server hosted on a local network requires understanding IP addressing, network configuration, and proper connection protocols. This guide walks through the essential steps for establishing reliable access to local servers.
How to Access a Server on Your Local Network: A Technical Guide
Accessing a server hosted on a local network is a fundamental skill for IT professionals, system administrators, and power users managing infrastructure within a closed environment. Whether you're running a development server, file storage system, or internal application, understanding how to properly connect to and access these resources is critical for productivity and security.
Understanding Local Network Architecture
A local network, or LAN (Local Area Network), connects devices within a limited geographic area—typically your home, office, or data center. Servers on this network operate independently from the public internet, making them accessible only to devices connected to the same network infrastructure.
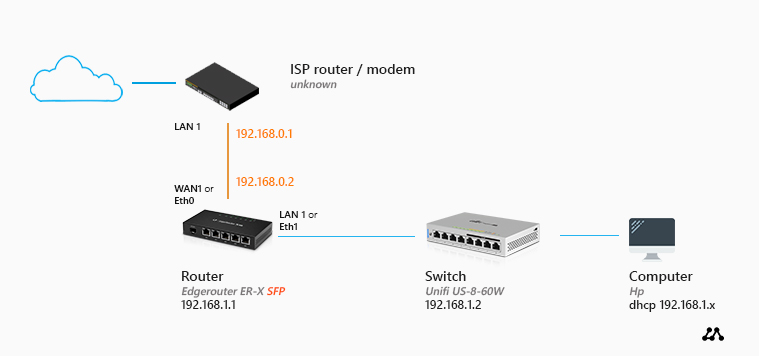
The foundation of local network access relies on IP addressing. Each device on your network, including servers, receives a unique IP address (either IPv4 or IPv6) that identifies it within that environment. These addresses typically fall within private ranges such as 192.168.x.x, 10.x.x.x, or 172.16.x.x to 172.31.x.x.
Prerequisites for Connection
Before attempting to access a local server, ensure you have:
- Network connectivity: Your device must be connected to the same physical network (via Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi)
- Server IP address: The specific address where your server is hosted
- Port information: The port number the server listens on (commonly 80 for HTTP, 443 for HTTPS, 22 for SSH, 3306 for MySQL)
- Credentials: Username and password if authentication is required
- Network permissions: Firewall rules that allow communication between your device and the server
Methods for Accessing Local Servers
Direct IP Address Connection
The most straightforward approach is entering the server's IP address directly into your browser or connection tool. For example, typing http://192.168.1.100:8080 in your web browser connects to a server at that address on port 8080.
Using Hostnames
Many networks implement DNS (Domain Name System) locally, allowing you to access servers by name rather than IP address. This approach is more user-friendly—accessing http://fileserver.local is simpler than remembering numeric addresses.
SSH and Remote Access
For command-line access to servers, SSH (Secure Shell) provides encrypted connections. Using a terminal, you can connect via ssh username@192.168.1.100, enabling full administrative control over the server.
VPN and Secure Tunneling
For remote access to local servers outside your physical network, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) create encrypted tunnels that make your device appear as if it's on the local network, allowing seamless server access from anywhere.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Connection Refused: Verify the server is running and listening on the specified port. Check firewall settings on both your device and the server.
Network Unreachable: Confirm your device is connected to the correct network and that both devices share network connectivity.
Slow Performance: Network congestion or hardware limitations may cause delays. Check bandwidth usage and consider upgrading network infrastructure if needed.
Authentication Failures: Double-check credentials and ensure your user account has appropriate permissions on the server.
Security Considerations
Local network access doesn't eliminate security requirements. Implement strong authentication, use encrypted protocols (HTTPS, SSH), and maintain updated firewall rules. Even internal servers should be protected against unauthorized access from compromised devices on your network.
Key Sources
- Network configuration best practices from IT infrastructure documentation
- TCP/IP and local networking standards from industry technical references
- SSH and remote access protocol specifications from security standards
Accessing local servers efficiently requires understanding both the technical mechanics and security implications. By following these guidelines and maintaining proper network hygiene, you can establish reliable, secure connections to your local infrastructure.


